- 22 Posts
- 21 Comments
So far this season…
Enjoying:
- Horimiya
- Zom 100
Waiting to see how it plays out:
- Vending machine
- Ryza
- One Room Hero
- Helck
Waiting to binge after the season is over:
- Kenshin
Old show I am currently watching:
- Science Fell in Love

 6·1 year ago
6·1 year agoYeah, even comments here haven’t seemed to read the article. As somebody that used to install BOINC on all my machines back in the day, the reason I stopped is that many of the projects I ran (SETI being one) aren’t active any longer. Also, like the article mentioned, I just don’t have a desktop anymore and I am not about to run something like this on a laptop that doesn’t have things like user-serviceable or replaceable parts.
 2·1 year ago
2·1 year agoI think that @saccharomyces@mander.xyz provided a great response for the specific case of flow in a pipe.
I just want to add that if you look beyond the restrictions of flow in a pipe, there are many other types of behavior that non-Newtonian fluids exhibit. We measure this in the lab on instruments called rheometers. Basically, we put some liquid in the instrument and then deform it and measure the resistance to that deformation. One of the most common ways to apply that deformation is to do so back and forth in an oscillating manner. Depending on the frequency at which you apply this strain, the solid/liquid-like behavior can change. If you have some background in physics or want to get a decent understanding, I found this paper that, on skimming it, seems to be pretty consistent with the way I was taught this stuff in grad school.
One graph I want to point out is Figure 13 which shows what would be a “typical” viscoelastic polymer solution. An easy way to understand this graph is that as we go from left to right, we are applying strain back and forth quicker and quicker, essentially shaking it faster. When the G’ value is higher than the G" value, then the material is behaving more like a solid and conversely, when G" > G’, then it is behaving more like a liquid. You can see that the material goes through different phases of behavior as the strain frequency changes. Just for you I went and dug up an old graph from my thesis to show a real-life example of this happening too.
My favorite demonstration of this is to put Oobleck (or something similar) onto a speaker and then change the frequency and see what happens.
Please, please let Ooyama’s accidental confession mean something. Imo, this series has really pushed the “do they like me” bit to the breaking point. If Akutsu goes back to questioning it, then it’s clear this series is never going to see real relationship progress.

 5·1 year ago
5·1 year agoThe fine is from an unrelated, earlier incident in Alabama. From what I found on jalopnik:
Earlier this year, a worker was killed by being sucked into an airplane engine in Alabama on New Year’s Eve. The employee in that scenario was warned several times that the plane’s engines would be on, however. Still, OSHA hit the small airline Piedmont with a fine of $15,625 in the workers death.
This incident with Delta that happened in Texas is under investigation.
 4·1 year ago
4·1 year agoI love Lichtenberg Figures as much as the next nerd, but knowing even a little bit about how they are made should make all the alarm bells in your head go off that it shouldn’t be done at home. If you want a safe way to play around with electricity, get a Van de Graaff generator.
That’s fair. I couldn’t find much info on their website, so I assumed this was another make insulin cheap using “biohacking” deal. I don’t have any experience with small molecule synthesis or dry powder manufacturing, so I can’t really speak to how feasible this may be. However, having seen first-hand all the ways simple manufacturing steps can go wrong, the risk of consuming a medication that hasn’t been through rigorous QA/QC makes me very wary.
Apologies for the long post. I don’t mean this as an attack on OP, just trying to illustrate why actually doing this is a bad idea.
I have seen efforts like this in the past, especially centered around efforts to manufacture insulin cheaply. While I get that medicine cost and availability is broken at a fundamental level in the US, the solution is a political one rather than to run a wildcat bioreactor. There is simply no way to safely manufacture biologics using a 3d printed bioreactor. Let’s look at the manufacturing process to get an idea of why.
Staring with the bioreactor, you would need some way to sterilize it before use (not just sanitize, there’s a difference). There are plastic bioreactors that are used in industry, but they are large, single-use bags that are sterilized using gamma or x-ray radiation. Most industry bioreactors are made of stainless steel to withstand the harsh treatment required to re-sterilize them (steam or hydrogen peroxide).
Moving down the chain from the bioreactor, you need some way to remove your product from the harvested liquid. This is usually done through lysing the cells you have grown and then running this lysate through a series of chromatography columns of varying types (affinity, ionic, etc.) to systematically remove all the junk left over from your cellular media and the cells you have lysed. Even if you could (unsafely) grow your cells and drug in a 3d printed bioreactor, you don’t have these kinds of things at home and can’t just get them from Amazon.
However, let’s say that you could get past the purification step, what’s next? You find yourself with a large volume of very dilute medicine suspended in a chromatography buffer. The next step is what is called UF/DF, or ultra-filtration/dia-filtration. This step, paradoxically done DF first, uses filter membranes and large amounts of buffer and some pressure to first swap out the buffer that your medicine is in to the target formulation that you want to inject and then concentrate it down to a manageable volume. If you are working at small scale, then you can probably replace this step with just one filter and a centrifuge. Remember that while you are doing all this, everything that comes into contact with your drug needs to be sterile (even the air).
I think I have made my point, but for actual drugs there are more steps beyond this. Post-UF/DF is what is referred to as drug substance (DS) in the industry. You still need to go through a sterile fill-finish process to get drug product (DP) that is what is actually given to a patient. If you really want, I can go on another long tirade here since this is the step my job focuses on.
I have worked on these manufacturing processes and seen them fail a lot for very hard to catch problems. Without all the in-process controls and testing we do, there would have been serious risks of giving bad DP to patients. If you have read this far, then I hope I’ve convinced you not to give this kind of thing a try.
The real problem this is trying to solve is a political one. We should be advocating for better access to medications and reforming how costs are dealt with. It doesn’t matter what your political persuasion is, I think everyone agrees healthcare in the US is broken and it’s time something is done about it.

 0·1 year ago
0·1 year agoThis might not quite be what you are looking for, but my favorite piece of writing that is science-adjacent is Surely You’re Joking, Mr. Feynman!.
As for current stuff, I work in pharma development, so there aren’t great sources out there. A lot of the studies that are published in places like phys.org or medicalxpress.com (or other wire-like services) pertain to very early stage drug discovery things, not formulation and device development. I tend to keep a tab open to fiercepharma and fiercebiotech for industry news. Other than that, there are a handful of academics that tend to share papers on linkedin or twitter that usually get passed around in the office if people find it interesting.

 4·1 year ago
4·1 year agoI am glad I don’t work in the clinical trial design space. It is already complicated enough to design a good clinical trial and this adds a whole other layer of complexity to it.
A sad component to this is that women are already underrepresented in clinical trials and this is likely to exacerbate the problem.
It hopefully should. One of the main reasons biologics are so expensive isn’t just corporate greed (though it is that too), but because the manufacturing process is very intense. Running bioreactors at commercial scale to make your product, using a train of chromatography steps to purify it, and then filtering it to be concentrated and sterile before fill/finish in a pre-filled syringe or vial followed sometimes by lyophilization is an insanely complicated process that is very costly. mRNA processes simplify this a lot in that the mRNA don’t need to be manufactured using bioreactors that are filled with dirty cellular flotsam and jetsam that need removed. So, the production and purification parts are much much simpler. It still isn’t likely to be cheap, as GMP manufacturing is still complex and the fill/finish part of the operations are largely unchanged, but hopefully cheaper.
This is neither here nor there, but I just want to compliment whoever did their favicon. I didn’t realize favicons could be animated like that, I am surprised I don’t see it more often.
I work in this field and this is a great summary of mRNA and its therapeutic usage. The article does mention it, but mRNA is going to be widely used beyond vaccines as well.
As an example, at a previous company I worked at that had a robust pipeline and a portfolio of antibodies on the market, they were actively developing an mRNA-LNP version of all of their mAb programs. The idea is that if you develop an LNP platform that can reproducibly transfect say, the liver, then you can just turn the liver into a protein factory for anything you provide the mRNA sequence for. Having mAbs produced and excreted in the body solves one of the big challenges to convenient biologics dosing, bioavailability. Basically, a lot of antibodies, when injected under the skin, have trouble making it from the injection site to your bloodstream. This can be solved by administering via IV, but that has many downsides when it comes to patient convenience.
The reason vaccines are the first successful application of this technology is because they only require very small doses to be effective. Compare the amount of protein that is in a flu shot (60 micrograms in Fluzone at most) to a typical mAb (~150 mg up to 1 g at most), you can see how much less the vaccine requires. I fully expect that as the upstream and downstream processes for LNP manufacture improve and are able to scale, that we will see mRNA take over what is currently the realm of biologics.

 3·1 year ago
3·1 year agoI added the link to the research paper above. Turns out the doi in the article is not correct.

 54·1 year ago
54·1 year agoBack in the olden days of reddit, mods didn’t need to accept their position. So, it was a troll tactic to promote people to moderator of a controversial sub and then take a screenshot. I have no knowledge of spez’s moderating history, but I imagine this is the most likely scenario.

 5·1 year ago
5·1 year agoThis pretty much lines up with my take as well. Educating borrowers via the first three bills on true costs, expected earnings, and repayment options is fine, but is mostly done already. I don’t see how mandating a form that needs to be signed saying that you understand the debt you are taking on is going to change that.
The fourth bill is pretty blatantly ideologically motivated. If they truly think that these programs are worth less, then a better solution might be something like tying the cost of tuition for different majors to the expected earnings potential rather than eliminating aid eligibility.
The fifth bill would have a dramatic impact on graduate students. I am lucky enough that I did my PhD back when a graduate student stipend could (just barely) cover living expenses. However, graduate student pay has not kept up with cost of living, and grad students often take out the PLUS loans to help bridge the gap. Eliminating these would essentially price out a lot of grad students in HCOL areas that don’t have family wealth to draw from. Alternatively (and preferentially), it could motivate schools to actually pay a living wage to grad students. However, the most likely outcome is that schools would just bring in more wealthy international students to fill the enrollment gap.

 1·1 year ago
1·1 year agoThanks for the explanation! I was curious how the targeting differed between the two mAbs and found a paper that explains:
Specifically, lecanemab mainly targets Aβ protofibrils, while aducanumab and other monoclonal antibodies favour highly aggregated forms of Aβ [5]. This differing target profile may also explain a substantially lower incidence of amyloid related imaging abnormalities, such as transient immunotherapy-related brain oedema and microbleeds, with lecanemab.
In other words, lecanemab seems to bind and remove Aβ before it aggregates, while other therapies (aducanumab) bind and then remove it after aggregation occurs.

 2·1 year ago
2·1 year agoGreat insight into the clinical process of Alzheimers care. I have worked on Amyloid programs before (early stage pharma R&D), and was wondering if there are significant clinical differences between lecanemab and aducanumab that makes you think this approval will have a less problematic trajectory? From my perspective, they are both mAbs targeting the same thing, but the discussion around lecanemab is different than it was for aducanumab, but perhaps that was primarily due to the non-standard phase 3 process of adu.
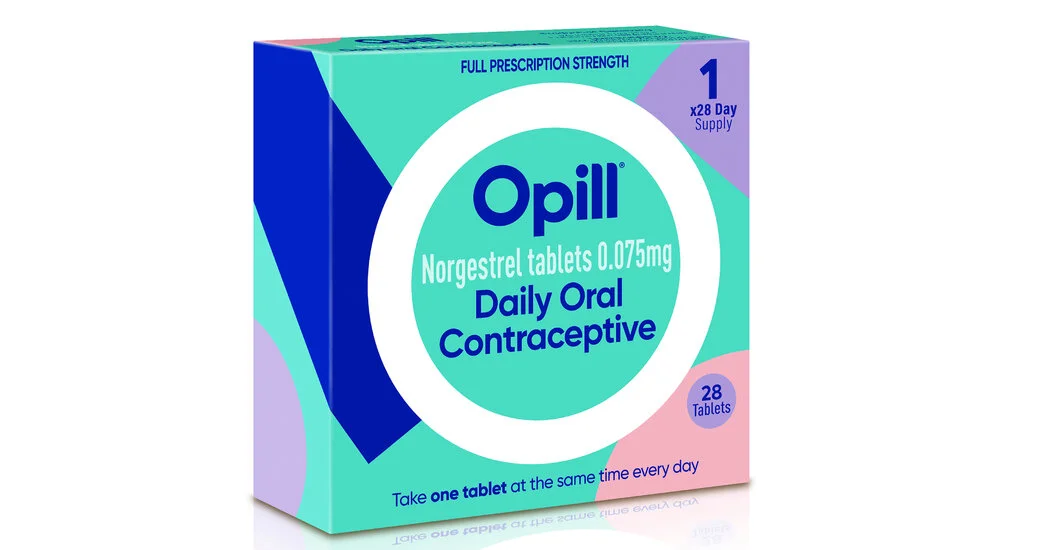



















The type of pill that was approved is the progestin-only “mini pill” which has a much safer clinical profile than the more common-in-the-US combination pill that has both progestin and estrogen. This type of pill is already available OTC in over 100 other countries. The US is just really behind the curve on just about anything to do with reproductive rights and care.